免疫学,肿瘤免疫治疗,体液免疫,抗体作用机制和优化,B淋巴细胞发育分化
体液免疫与治疗实验室的研究主要有两个方向:(一)肿瘤免疫治疗抗体作用规律和优化策略;(二)B淋巴细胞的发育调控机制。
肿瘤免疫治疗
肿瘤的免疫治疗是过去十年取得的最有希望的科学进步之一,被《科学》杂志评选为2013年“年度突破”。目前主要有四种手段可以利用免疫系统的力量来对抗肿瘤:1)针对肿瘤抗原的抗体被输入到肿瘤病人体内杀灭肿瘤细胞,其中部分机制是肿瘤细胞结合了抗体之后被表达Fc受体的免疫细胞杀灭;2)从肿瘤病人分离的抗肿瘤免疫细胞在体外扩增(有时候还被基因修饰),然后回输到病人体内发挥抗肿瘤作用;3)T细胞被基因工程修饰后表达识别肿瘤抗原的嵌合抗原受体(Chimeric Antigen Receptor,CAR)被输入到肿瘤病人体内;4)利用单克隆抗体(单抗)阻断限制免疫细胞活性的免疫抑制信号通路(被称为“节点”)从而提高免疫细胞的活性。
激动型抗体:一类具有广泛前景的肿瘤免疫治疗抗体
体液免疫与治疗实验室的一个主要研究兴趣是激动型肿瘤免疫治疗抗体的作用规律和优化策略。已经研发成功的肿瘤免疫治疗药物包括抗CTLA-4与抗PD-1/PD-L1 抗体,它们都通过阻断免疫细胞表面传递免疫抑制信号的分子的作用增强免疫系统针对肿瘤细胞产生的杀伤性T细胞应答从而杀伤肿瘤,属于阻断型抗体。而除此之外,还有一类被称为“激动型抗体”的肿瘤免疫治疗手段,能够通过结合免疫细胞表面传递免疫激活信号的靶标分子并激活其控制的重要免疫激活信号通路,进而增强抗肿瘤免疫应答间接杀死肿瘤细胞。然而,虽然激动型肿瘤免疫治疗抗体已经在动物模型中证明了其巨大潜力,并且已经成为一个被广泛接受并看好的肿瘤免疫治疗理念,这类抗体的研发至今尚未成功,是肿瘤免疫治疗领域当前的一个主要挑战。纠其原因,可能与这类抗体的体内作用条件不明有关。在基于鼠类激动型抗肿瘤抗体的研究中,我们发现了一条可能有助于研发具有较好抗肿瘤活性的激动型抗体的线索,即这些抗体的Fcγ受体(Fcγ receptor,或FcγR)结合能力对它们的抗肿瘤活性具有决定性的影响,现在正在展开研究。
Fcγ受体的体液免疫与治疗调控功能
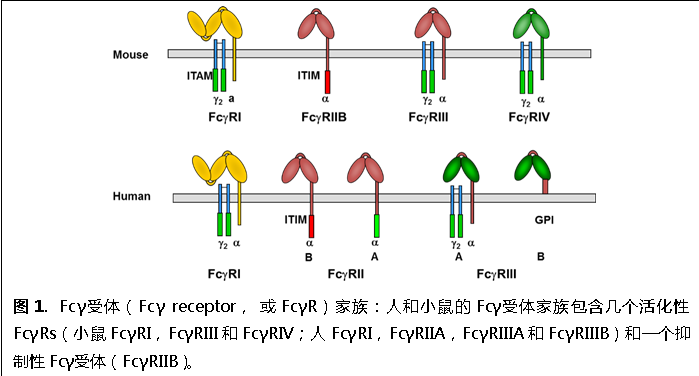
Fcγ受体与IgG抗体相互作用,是IgG抗体治疗作用的重要介导者和调控者;同时,Fcγ受体与含有IgG的免疫复合物相互作用,调控免疫应答的传入和传出,如对B细胞应答的调控。Fcγ受体广泛表达在免疫细胞表面,介导抗体的免疫调控和效应功能。人和小鼠的FcγR家族都由几个活化性FcγRs(activating FcγRs)和一个抑制性Fcγ受体(Inhibitory FcγRIIB,或FcγRIIB)组成(图1)。抑制性Fcγ受体胞内区含有酪氨酸依赖的抑制型基序(Immunoreceptor Tyrosine-based Inhibitory Motif,或ITIM)传递抑制信号,起抑制细胞激活的作用。活化性FcγRs通过含有酪氨酸依赖的激活型基序(Immunoreceptor Tyrosine-based Activation Motif,或ITAM)的胞内区或Fc受体γ链(Fc receptor γ chain)传递活化信号,促进细胞激活。大量的实验已经证明活化性FcγRs在IgG抗体的效应功能中发挥主导作用。例如,抗体依赖细胞介导的细胞毒性作用(Antibody-Dependent Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity,或ADCC)就是通过活化性FcγRs完成的。ADCC是效应型治疗抗体重要的肿瘤杀伤机制,对这类抗体(如Rituximab)的疗效有显著影响。
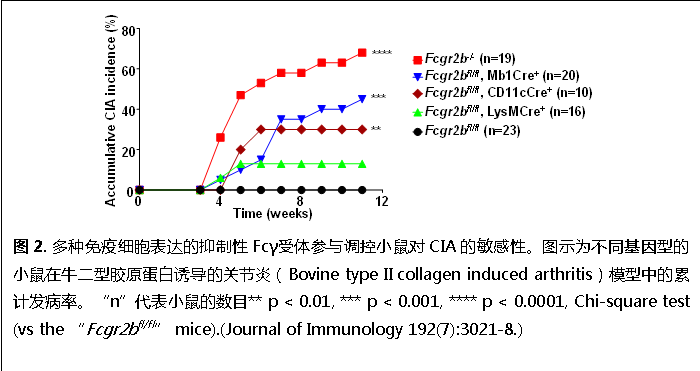
我们发现抑制性Fcγ受体能够对多种免疫细胞的调控对免疫耐受的维持都具有显著影响(Li et al. 2014. Journal of Immunology 192(7):3021-8.),如在B细胞与树突状细胞(dendritic cells)中特异敲除抑制性Fcγ受体致使小鼠在CIA(collagen induced arthritis)自身免疫模型中更加敏感(图2).此外,人类抑制性Fcγ受体的功能受损被发现与包括系统性红斑狼疮、风湿性关节炎等多种自身免疫疾病。
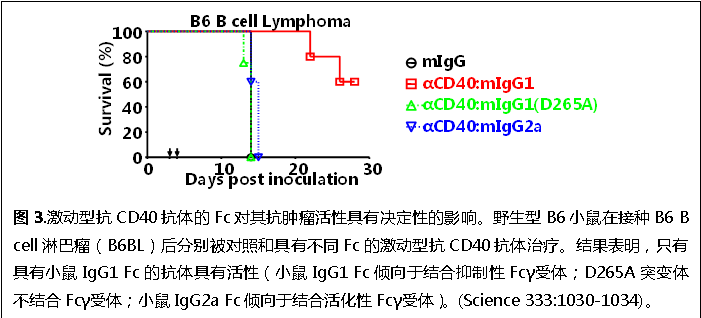
我们还系统研究了Fc-FcγRs相互作用对激动型抗TNF受体超家族成员抗体(agonistic anti-TNFR antibodies)分子的体内活性的影响。以激动型抗CD40和DR5抗体为例,我们发现这类抗体的体内活性依赖于Fcγ受体分子,而且抗体Fc的属性对其体内抗肿瘤活性具有决定性的影响(图3)。
进一步研究表明,与依赖于活化性Fcγ受体的效应型抗体不同,激动型抗TNFR抗体体内活性只依赖于抑制性Fcγ受体,而与活化性FcγRs的相互作用会降低其活性。在此基础上,我们提出了一种优化激动型抗TNFR超家族成员抗体的方法(图4)
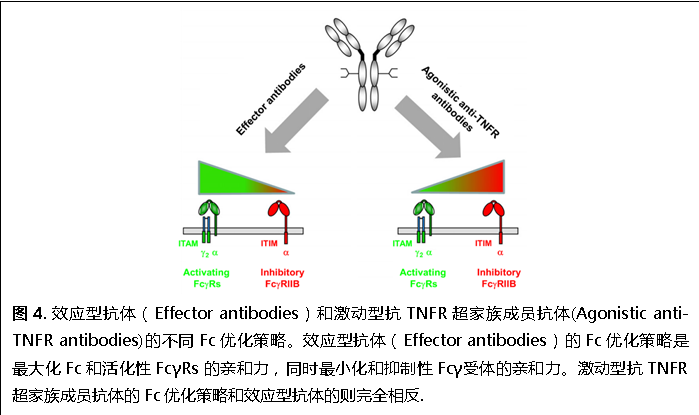
:最大化与抑制性Fcγ受体的结合亲和力,同时最小化与活化性FcγRs的结合亲和力,和传统的优化效应型抗体的方法刚好相反。用这种方法优化的人抗小鼠CD40抗体都已经在人抑制性Fcγ受体转基因小鼠模型中得到了验证(图5)。
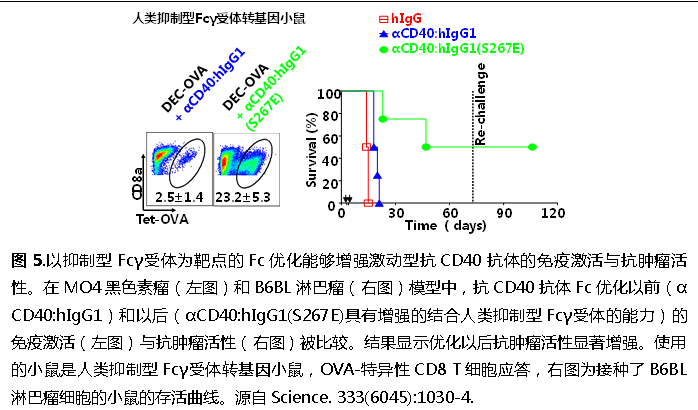
这些成果被连续发表在包括2011年Science(Li, F., and J.V. Ravetch. 2011. Science 333:1030-1034),2012年PNAS杂志(Li, F., and J.V. Ravetch. 2012. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 109:10966-71),和2013年PNAS杂志(Li, F., and J.V. Ravetch. 2013. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 110:19501-6),和2016年Cancer Cell杂志(Dahan, R., B. C. Barnhart, F. Li, A. P. Yamniuk, A. Korman, J.V. Ravetch. 2016. Cancer Cell),并受邀在Cell Cycle杂志上就这一研究领域的进展发表评论文章(Li, F., and J.V. Ravetch. 2012. Cell cycle 11:18)。这些研究结果为解释尚未成功的激动型抗TNFR抗体研发提供了一条线索,可能有利于研发基于这类抗体的抗肿瘤药物。
目前,实验室工作的重点是进一步研究肿瘤免疫治疗抗体作用规律和优化策略,包括Fcγ受体相关和其它的调控规律和策略;同时,实验室对B淋巴细胞的发育调控规律也非常感兴趣,正在开展Fcγ受体及相关分子对体液免疫的调控机制。
1. Li, M., Lazorchak, A.S., Ouyang, X., Zhang, H., Liu, H., Arojo, O.A., Yan, L., Jin, J., Han, Y., Qu, G., Xu, X., Liu, X., Zhang, W., Wang, Q., Liu, D., Li, F.#, Su, B., .Sin1/mTORC2 regulates B cell growth and metabolism via mTORC1 and Myc activation..Cellular & Molecular Immunology,2019,16(9):757-769. [Link]
2. Wenqian Zhang, Huihui Zhang, Shujun Liu, Fucan Xia, Zijian Kang, Yan Zhang, Yaoyang Liu, Hui Xiao, Lei Chen, Chuanxin Huang, Nan Shen, Huji Xu, and Fubin Li.Excessive CD11c+Tbet+ B cells promote aberrant TFH differentiation and affinity-based germinal center selection in lupus.PNAS,2019,116 (37) 18550-18560. [Link]
3. Xiaobo Liu, Yingjie Zhao, Huan Shi, Yan Zhang, Xueying Yin, Mingdong Liu, Huihui Zhang, Yongning He, Boxun Lu, Tengchuan Jin & Fubin Li.Human immunoglobulin G hinge regulates agonistic anti-CD40 immunostimulatory and antitumor activities through biophysical flexibility.Nature Communications,2019,4206. [Link]
4. Dahan, R., B. C. Barnhart, F. Li, A. P. Yamniuk, A. Korman, J.V. Ravetch. .Therapeutic activity of agonistic, human anti-CD40 monoclonal Abs requires ive FcγR-engagement. .Cancer Cell ,2016,29(6):820-831. [Link]
5. Georgoudaki, A.M., K. Prokopec, E. Hellqvist, V. Boura, J. Östling, S. Sohn, R.A. Harris, M. Rantalainen, D. Klevebring, M. Sund, J. Fuxe, C. Rolny, F. Li, J.V. Ravetch, M.C.I. Karlsson. .Reprogramming tumor associated macrophages by antibody targeting inhibits cancer progression and metastasis. .Cell Reports ,2016,15(9):2000-11. [Link]
6. Deng Z, Ma S, Zhou H, Zang A, Fang Y, Li T, Shi H, Liu M, Du M, Taylor PR, Zhu HH, Chen J, Meng G, Li F, Chen C, Zhang Y, Jia XM, Lin X, Zhang X, Pearlman E, Li X, Feng GS, Xiao H. .Tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2 mediates C-type lectin receptor-induced activation of the kinase Syk and anti-fungal TH17 responses..Nature Immunology,2015,16:642-52. [Link]
7. Li, F#., P. Smith, and J. V. Ravetch#. .Inhibitory Fcgamma Receptor Is Required for the Maintenance of Tolerance through Distinct Mechanisms. .Journal of immunology ,2014,192:3021-8 . [Link]
8. Simpson, T. R., F. Li, W. Montalvo-Ortiz, M. A. Sepulveda, K. Bergerhoff, F. .Fc-dependent depletion of tumor-infiltrating regulatory T cells co-defines the efficacy of anti-CTLA-4 therapy against melanoma.The Journal of experimental medicine,2013,210: 1695-1710. [Link]
9. Li, F#., and J. V. Ravetch#. .Antitumor activities of agonistic anti-TNFR antibodies require differential FcgammaRIIB coengagement in vivo. .Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2013,110: 19501-19506. [Link]
10. Smith, P., D.J. Dilillo, S. Bournazos, F. Li, and J.V. Ravetch.Mouse model recapitulating human Fcgamma receptor structural and functional diversity. .Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America ,2012,109:6181-6186. [Link]
11. Li, F., and J. V. Ravetch.Apoptotic and antitumor activity of death receptor antibodies require inhibitory Fcgamma receptor engagement..Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America ,2012,109: 10966-10971. [Link]
12. Li, F., and J. V. Ravetch.A general requirement for FcgammaRIIB co-engagement of agonistic anti-TNFR antibodies..Cell cycle ,2012,11: 3343-3344. [Link]
13. Li, F., and J.V. Ravetch.Inhibitory Fcgamma receptor engagement drives adjuvant and anti-tumor activities of agonistic CD40 antibodies. .Science ,2011,333:1030-1034. [Link]
14. Li, F., Y. Yan, J. Pieretti, D.A. Feldman, and L.A. Eckhardt. .Comparison of identical and functional Igh alleles reveals a nonessential role for Emu in somatic hypermutation and class-switch recombination. .Journal of immunology ,2010,185:6049-6057. [Link]
15. Li, F., and L.A. Eckhardt.A role for the IgH intronic enhancer E mu in enforcing allelic exclusion.The Journal of experimental medicine ,2009,206:153-167. [Link]
16. Zhang, B., A. Alaie-Petrillo, M. Kon, F. Li, and L.A. Eckhardt.Transcription of a productively rearranged Ig VDJC alpha does not require the presence of HS4 in the IgH 3 regulatory region. .Journal of immunology ,2007,178:6297-6306. [Link]
17. Romov, P.A., F. Li, P.N. Lipke, S.L. Epstein, and W.G. Qiu..Comparative genomics reveals long, evolutionarily conserved, low-complexity islands in yeast proteins. .Journal of molecular evolution,2006,63:415-425. [Link]
18. Garrett, F.E., A.V. Emelyanov, M.A. Sepulveda, P. Flanagan, S. Volpi, F. Li, D. Loukinov, L.A. Eckhardt, V.V. Lobanenkov, and B.K. Birshtein.Chromatin architecture near a potential 3 end of the igh locus involves modular regulation of histone modifications during B-Cell development and in vivo occupancy at CTCF sites.Molecular and cellular biology,2005,25:1511-1525. [Link]
 沪公网安备 31009102000053号 沪ICP备18007527号-1 邮箱:sii@sjtu.edu.cn
沪公网安备 31009102000053号 沪ICP备18007527号-1 邮箱:sii@sjtu.edu.cn