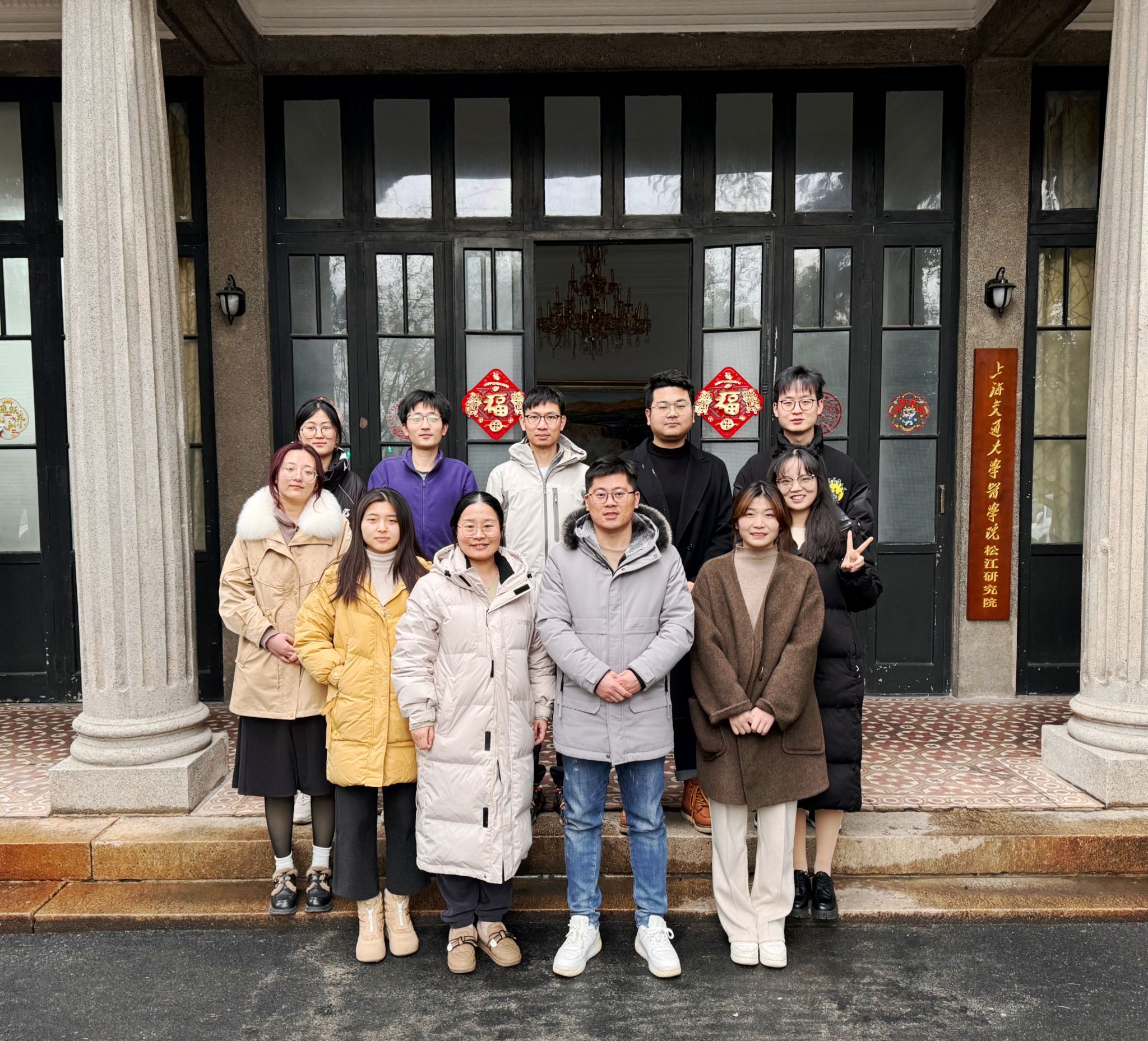
Wenjie Zhou, Ph.D., Investigator
Work Phone: 86-21-67722465
E-mail: zhouwj2022@shsmu.edu.cn
Neural circuits of cross-modality modulation
Educational Experience
2012-2019 University of Science and Technology of China (Ph.D. in Neuroscience),
2009-2013 Anhui University (B.S. in Biology)
Professional Experience
2022-12 - present Investigator, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine
2022-01 - 2022-11 Associate Research Fellow, University of Science and Technology of China
2019-2021 Postdoctoral Fellow, University of Science and Technology of China
 Wenjie Zhou
Wenjie Zhou
The sensory nervous system processes stimuli in different modalities (e.g. visual, olfactory, auditory, and somatosensory) and is the basis of our brain to perceive the external environment. Meanwhile, our brain executes top-down control to regulate physiological functions of our body. However, the cross-modal interactions between distinct sensory processing and their roles in regulating physiological function remain largely unknown. Our laboratory is devoted to exploring neural mechanisms underpinning bi-directional interactions between different sensory perceptions, and immune, endocrine and emotional systems. By combining multiple cutting-edge tools, we aimed to identify novel approaches to treat neurological diseases with striking effect and less side effect.
1. Neural circuits mediating cross-modal interactions
The sensory nervous system is the basis for perceiving the environment and enables us to learn, feel and enjoy life. We aim to dissect the neural circuits underpinning the cross-modal interactions between different sensory processing under physiological and pathological conditions.
2. Neural circuits underlying sensory and emotional interaction
Somatosensory (pain), auditory (music), olfactory (odor) and visual (light) stimuli can affect our emotions. Therefore, we aim to unveil the neural circuits of how distinct
sensory stimuli affect emotions (pleasure or aversion), with the hope to develop new adjuvant therapy for treating emotional disorders.
3. Mechanisms for interactions between the central neural system and the peripheral endocrine system under pathological states
The central neural system dictates the peripheral immune and endocrine systems. We are committed to investigate mutual interactions between the peripheral immune and endocrine systems and the central nervous system under pathological states such as depression and chronic pain.
-
 Lixing Lu ,PhD student
Email:lixinglu_hannah@163.com
Research Direction:Neural mechanism of sound regulates emotion through the heart-brain axis
Lixing Lu ,PhD student
Email:lixinglu_hannah@163.com
Research Direction:Neural mechanism of sound regulates emotion through the heart-brain axis
-
 Menghui Guo,Research Assistant
Email:guomenghui98@126.com
Research Direction:1. Neuroimmunopharmacology; 2. Research on the mechanism of visual regulation of heart rate changes.
Menghui Guo,Research Assistant
Email:guomenghui98@126.com
Research Direction:1. Neuroimmunopharmacology; 2. Research on the mechanism of visual regulation of heart rate changes.
-
 Zhihua Luo,postdoctor
Email:luozhihuagd@163.com
Research Direction:Study on neural circuit mechanism of auditory system regulating emotion;
Zhihua Luo,postdoctor
Email:luozhihuagd@163.com
Research Direction:Study on neural circuit mechanism of auditory system regulating emotion;
-
 Hongzhi Liu,Postdoctor
Email:pd342150@shsmu.edu
Research Direction:1. Neural mechanisms of fear of height 2. Cancer neuroscience
Hongzhi Liu,Postdoctor
Email:pd342150@shsmu.edu
Research Direction:1. Neural mechanisms of fear of height 2. Cancer neuroscience
-
 Yingwei Gao ,associate research fellow
Email:yingweigao@163.com
Research Direction:1. Central regulatory mechanism of pain; 2. Molecular mechanisms of TRP channels in peripheral pain and itch sensation.
Yingwei Gao ,associate research fellow
Email:yingweigao@163.com
Research Direction:1. Central regulatory mechanism of pain; 2. Molecular mechanisms of TRP channels in peripheral pain and itch sensation.
-
Zhou W#, Ye C#, Wang H#, Mao Y#, Zhang W, Liu A, Yang C, Li T, Hayashi L, Zhao W, Chen L, Liu Y*, Tao W*, Zhang Z* (2022). Sound induces analgesia via corticothal amic circuits. Science 377:6602.

-
Zhou W#, Jin Y#, Meng Q#, Zhu X#, Bai T, Tian Y, Mao Y, Wang L, Xie W, Zhong H, Zhang N, Luo M, Tao W, Wang H, Li J, Li J, Qiu B, Zhou J, Li X, Xu H, Wang K, Zhang X, Liu Y, Levin G, Xu L, Zhang Z* (2019). A neural circuit for comorbid depressive symptoms in chronic pain. Nat Neurosci 1649-58.

-
Zhu X#, Zhou W#, Jin Y, Tang H, Cao P, Mao Y, Xie W, Zhang X, Zhao F, Luo M, Wang H, Li J, Tao W, Farzinpour Z, Wang L, Li X, Li J, Tang Z, Zhou C, Pan Z*, Zhang Z* (2019). A central amygdala input to the parafascicular nucleus controls comorbid pain in depression. Cell Rep 3847-58.

-
Meng X#, Yue L#, Liu A#, Tao W, Shi L, Zhao W, Wu Z, Zhang Z, Wang L*, Zhang X*, Zhou W* (2022). Distinct basolateral amygdala excitatory inputs mediate somatosensory and aversive-affective components of pain. J Biol Chem 298:102207.








 Location:
Location:
